In addition to the TPC-H workload for Oracle, PostgreSQL and MySQL there are also a set of Cloud Analytic Queries made publicly available by Oracle for comparison of Cloud Analytic services. These queries run against a TPC-H schema and are included with HammerDB for running against Oracle, Amazon Aurora and Amazon Redshift with Amazon Aurora and Redshift being based upon and compatible with MySQL and PostgreSQL respectively. Note however that in similarity to MySQL Amazon does not have the features to support analytics such as parallel query or a column store option and therefore running the analytic tests against Aurora although possible is not likely to generate the best results. Amazon Redshift however is a column oriented database based on PostgreSQL and suitable for running analytic workloads.
For the Cloud Analytic workload the database is created and loaded according to the TPC-H specification – HammerDB by default can create and load schemas of scale factor 1, 10, 30, 100, 300 and 1000 which corresponds to 1GB, 10GB, 30GB, 100GB, 300GB and 1TB respectively. HammerDB will create the schema and load the data. The time this takes is dependent on multiple factors – in particular storage performance is a key factor for inserting a large number of rows into the database as each insert requires redo logging and there is the potential for contention as the number of virtual users increases all inserting rows into the same table at the same time. For this reason especially as the Oracle specification requires a schema size of 10TB, it is recommended to create the schema with HammerDB using the Generating and Bulk Loading Data feature and this guide details how to do this for both Oracle and Redshift and this is particularly recommended when uploading data to the cloud.
You are permitted to run both the in-built TPC-H query workload and the Oracle provided query set against any size schema however the Oracle workload provides 13 new analytic queries – that is run in sequence as per the original power test of TPC-H. This new query set compatible with Oracle, Redshift/PostgreSQL and MySQL/Aurora is enabled under the TPC-H Driver Script Options dialog by selecting the Cloud Analytic Queries checkbox. This query set reports the geometric mean of the completed queries that returns rows for circumstances where the query set is run on a scale factor size of less than 10TB. Given the similarity of the Oracle implementation to the existing TPC-H workload the following example illustrates running the workload against Amazon Redshift.
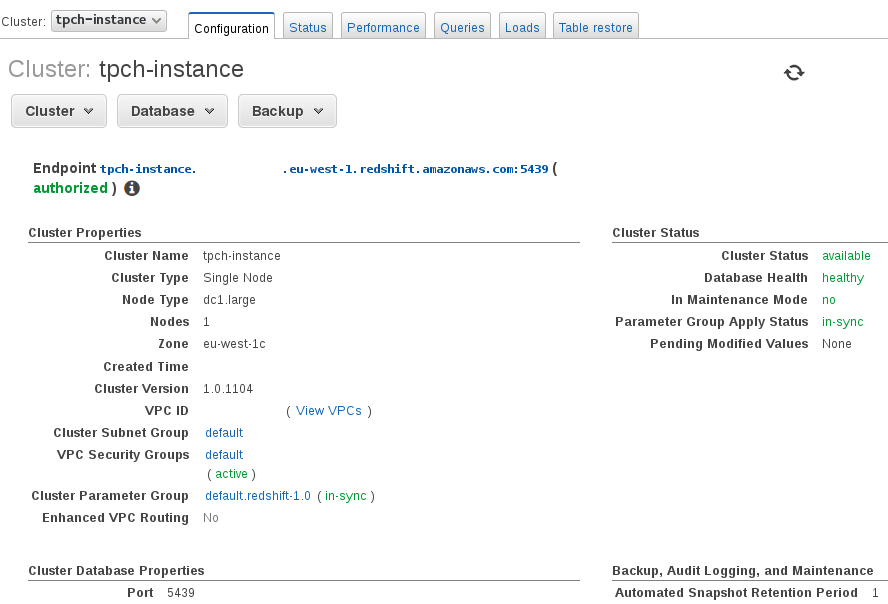
Ensure that your Redshift cluster is active and note your Endpoint name given above the cluster properties.
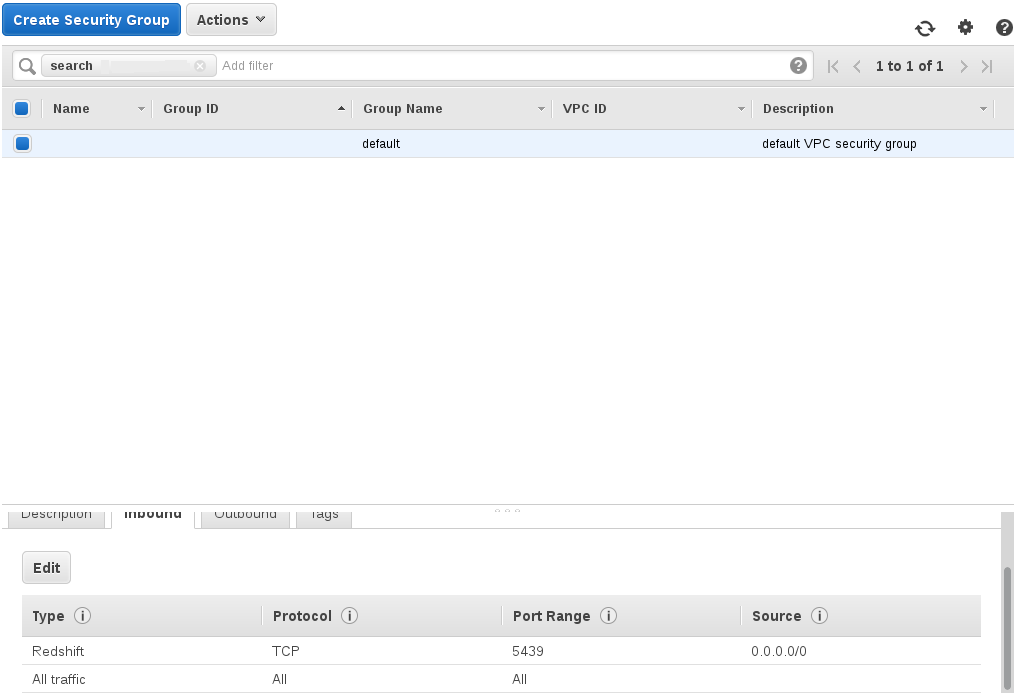
Also ensure that access is enabled to the cluster both by defining a user and a security group and allowing access through your firewall.
Create the TPC-H schema within Redshift using the HammerDB Generating and Bulk Loading Data feature. Under PostgreSQL TPC-H Driver Options use the Redshift Endpoint as your PostgreSQL host and 5439 as your port. Set the user and password to the credentials you have set under the Amazon AWS console. To run the Cloud Analytic Workload with HammerDB refer to the following Chapter on How to run an Analytic Workload and select the Cloud Analytic Queries and Redshift Compatible Checkbox with the reported metric being the geometric mean of the query times that complete for the one Virtual User used. Note that when running the queries against data sets smaller than the specified 10TB this may result in some queries not returning rows, therefore for your calculations HammerDB calculates the geometric mean only of queries that returned rows.